Biosimilar medicines: Overview
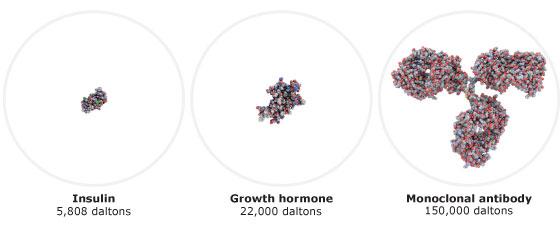
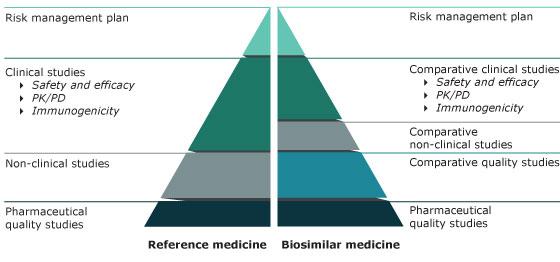
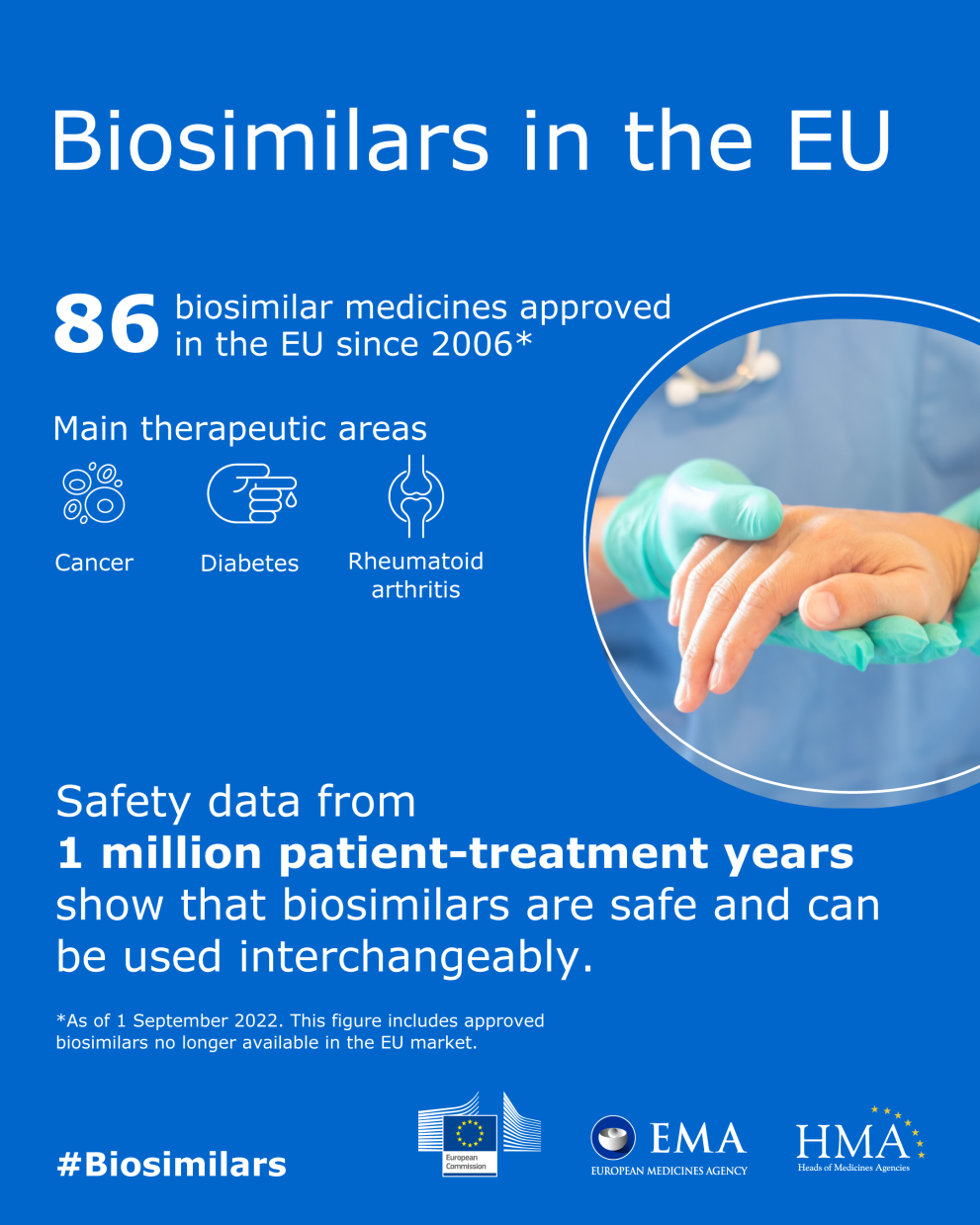
A biosimilar is a biological medicine highly similar to another already approved biological medicine (the 'reference medicine'). Biosimilars are approved according to the same standards of pharmaceutical quality, safety and efficacy that apply to all biological medicines. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is responsible for evaluating the majority of applications to market biosimilars in the European Union (EU).
HumanBiosimilarsRegulatory and procedural guidance